We have all experienced the feeling of a sudden sense of pain striking our teeth while drinking a cold refresher. The least fortunate of us have also encountered long-term, throbbing pain which makes the day really hard to endure.

To discover what causes sick teeth, we should contact our dentist as soon as possible. Until the examination we can ease the pain with painkillers containing ibuprofen, gels with local analgesic effect or a cold compress pressed on the jaw.
This article will answer the following questions:
- Diseases which can cause toothache
- When to turn to a doctor with a sick teeth?
- How to ease the pain of sick teeth?
What is toothache?
Just a few people have not experienced this so far. Many regard toothache for unbearable like the pain at childbirth. The reason for the pain is that there are lots of nerve fibres in the mouth that immediately and sometimes intensively react to the problems or alterations in the oral cavity.
What can the cause of toothache be?
There are numerous types of toothache. The most frequent type is the shrewd pain which occurs while eating cold or hot food and it strikes like a lightning. The cause can be – among others – incipient dental caries or damage to the dental filling.This chapter, however, reveals some other factors as well.You should contact your dentist as soon as possible because if the inflammation reaches the deeper layer of the tooth, it can lead to the inflammation of the root.
Dental diseases
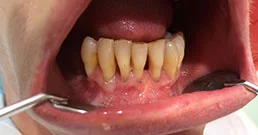 Dental caries, the inflammation of the root, a chipped tooth, damage or detachment of the filling and tooth grinding can all cause pain.
Dental caries, the inflammation of the root, a chipped tooth, damage or detachment of the filling and tooth grinding can all cause pain.
The initial symptom of caries can be intense pain experienced while eating cold or hot food. A revealing symptom is the discolouring of the affected tooth, unpleasant breath odour or swollen gums.
The inflammation of the root is a disease caused by bacterial infection. It is accompanied by very intense pain. Its symptoms can include fever, bitter taste, red, swollen gums, swollen face in the affected area and the pain getting stronger during chewing. To end the infection, local antibiotic treatment and later root canal treatment might be necessary.
In case of chipped teeth or detached filling, the main risk is bacterial infection, because the uncovered pulp loses its protection.
In its initial stage, tooth grinding involves jaw pain in the morning. In case of lasting grinding, the teeth can be damaged and they will be more susceptible to bacterial infections.
We can also experience this feeling after dental interventions.
If it doesn’t disappear after four weeks, we should contact our dentist. Intense pain during chewing can be a sign of caries or even of damage to the pulp. The cause of the pain which lasts for more than 30 minutes can be serious damage to the pulp. If even touching the teeth triggers intense pain, the problem might be the contagious disease of the gum.
By starting therapy as soon as possible, we can prevent serious complications like tooth loss or the expansion of the bacterial infection.
Gum diseases
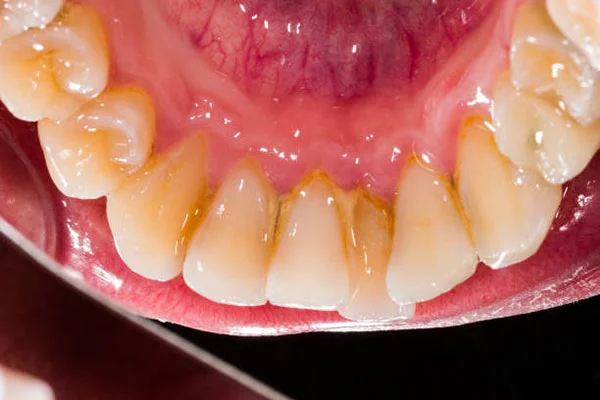 The inflammatory diseases of the gum are usually caused by bacterial infection. If you don’t seek treatment, this can lead to constant pain as well as tooth loss.
The inflammatory diseases of the gum are usually caused by bacterial infection. If you don’t seek treatment, this can lead to constant pain as well as tooth loss.
After eating, bacteria can spread in the pieces of food stuck to the teeth and dental plaque can form on the teeth. From this, bacteria can easily infect the gum and cause inflammation.
There are factors which facilitate the development of gum inflammation. During hormonal changes – in case of pregnancy, during puberty or menopause – we are more susceptible to the disease. A change resulting in the reduced defensive capabilities of the immune system also increases the probability of the disease, for example in case of HIV infection or cancer such as leukemia. In case of diabetes, the disease can develop more easily due to the circulatory disorder. The side effects of some medicines can also make us more susceptible to gingivitis. Also, smoking is a high risk factor for gum disease.
The symptoms of gingivitis are bleeding, swollen, aching gums, bad breath and moving teeth.
Treatment depends on how serious the disease is. Therefore you should turn to a specialist to establish the appropriate therapy. During and after the treatment you should ensure sufficient oral hygiene to reduce the chances of a return of the disease.
Diseases which can cause toothache
In case of angina pectoris, the heart does not receive a sufficient amount of blood. The organism signals this problem with a typical chest pain. In some cases this chest pain can spread to the teeth and the jaw as well. If you feel weakness, dizziness or nausea besides chest and tooth pain, you should see a cardiologist.
In case of sinus infection, we can experience pain in the upper set of teeth, especially in the molars. If the pain is accompanied by general adynamia and nose congestion, we should visit our GP in order to establish an exact diagnosis.
The pain originating from ear inflammation can radiate to the teeth on the affected side. We should visit our GP to start treatment as soon as possible.
The types of toothache
Do not try to make a diagnose between the type of pain and the cause of the problem. Our article aims to reveal which pain refers to which disorder.
Acute pain
A number of minor dental problems can cause acute pain. These include tooth decay with a broken tooth, a poorly placed crown, a too high filling, gnashing of teeth, and the consumption of cold or hot drinks and food. It is recommended to see a specialist diagnose the causes.
Temporary, so sharp toothache lasting for a few days can be observed after the tooth filling.
Dull pain
Dull pain usually indicates more serious problems; it can even mean damage to the nerve in the tooth. Dull pain can also be caused by, for example, tooth decay or other injuries, joint disorders of the jaw, gnashing of teeth, hot or cold foods and drinks.
We can see that there are overlaps between the causes of the previous two groups, so keep it in mind that the exact diagnosis can be made by our dentist.
Throbbing and intense pain
Typically, throbbing and intense pain refers to the most severe cases: more severe inflammations, infections, or abscesses. The pain is often accompanied by swelling. We recommend that you contact a specialist as soon as possible!
When to turn to a doctor with sick teeth?
We should always turn to a doctor in order to find out what causes the pain. In some cases, an immediate intervention is required.
We cannot postpone the examination if:
- the pain lasts longer than 1 or 2 days
- the pain is very intense
- you experience fever or earache
- the pain is stronger when opening the mouth
- pain is caused by chipped tooth or an injury to the jaw
How to ease the pain of sick teeth?
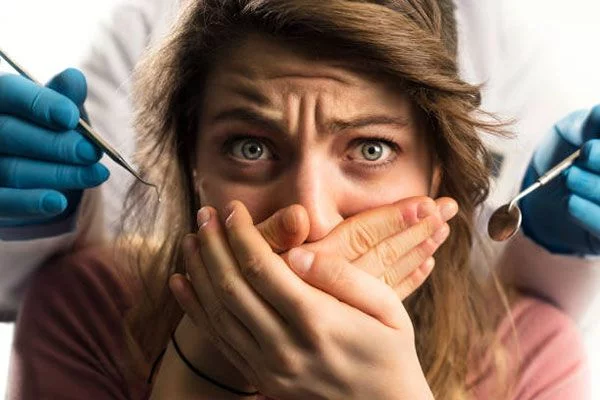 Until we get to the examination at the dentist’s, we can ease our pain in several ways. Painkillers containing ibuprofen or paracetamol ease our pain for 6 hours. It is important that we take the pills according to the instructions. We shouldn’t chew on them in the painful area.
Until we get to the examination at the dentist’s, we can ease our pain in several ways. Painkillers containing ibuprofen or paracetamol ease our pain for 6 hours. It is important that we take the pills according to the instructions. We shouldn’t chew on them in the painful area.
We can also use a gel with local analgesic effect. This makes the affected area a bit numb for a while. However, it is important that we only use this method for a short time.
A cold compress on the outside of our jaw will also ease pain. We should not use this method for more than 15 minutes at once. The best way is to apply the cold compress for shorter periods several times.
Traditional healing methods to ease the pain include:
- Put a bunch of cotton soaked in oil to the painful area and chew on it. It will make the painful area numb.
- Chew clove or rinse with clove oil. Besides its antibacterial effect it also numbs the sensitive teeth. In a similar way you can also use onion or garlic.
- Rinse with salty water. Put a teaspoonful of salt in 250 ml of warm water and keep it in your mouth for 30 seconds before spitting it.
- Soak a sterile bunch of cotton in a drink with high alcohol volume (vodka, brandy) and put it on the sensitive area.
It is best to avoid tooth and gum diseases. To avoid sick teeth we should brush our teeth regularly, twice a day, using floss for more effective cleaning and rinsing with water or mouthwash.