You might have wondered what the term dental bone graft means, in what cases it is necessary and how much the costs are. Our article provides answers to the following questions:
- When bone defects appear and what their main symptoms are
- How is a bone graft performed?
- When is a bone graft necessary?
- What risks are involved?
- What bone graft types are there?
- Costs of dental bone grafting
When bone defects appear and what their main symptoms are
A long-lasting prosthesis, a far-gone periodontal disease, or tooth loss in an accident can lead to bone defects. In the beginning, the damage is hardly recognisable because tooth loss does not really come together with significant pain. The main symptoms of far gone bone defects are bleeding gum, sensitive and swollen palate, bad breath, loose teeth, and weakening bites.
How is a bone graft performed?
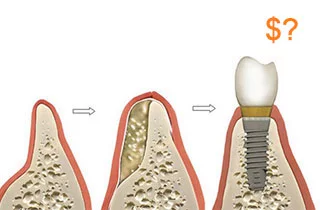
During bone grafting, the missing bone in the jaw is augmented. Following the medical tests taken before the intervention, an evaluation is made. Based on this evaluation, the doctor can decide whether the augmentation of the jaw bone is necessary for implantation or not. If it is, it must be clear how much bone is missing, and accordingly, how much bone would have to be replaced. After the successful operation, the new bones are able to develop in the body. Bone grafting is a process during which the dentist makes smaller or bigger incisions on the patient’s body. Thereafter, the material necessary to the regeneration of the bone is applied and the wound is closed.
The procedure consists of the following 4 steps:
- First, local anesthesia is performed. Then the surgeon opens the patient’s gingiva (gum) so that the bone can be accessed.
- During the second step, the doctor fills the area in question with a bone replacement substance.
- Last but not least, an artificial membrane is applied. It promotes the healing of the wound and accelerates recovery.
- The fourth and last step is the recovery period following the surgery; it may take 3-9 months.
When is a bone graft necessary?
As it has been previously indicated, the most common reason for bone tissue atrophy is the absence of tooth or teeth. Losing a tooth means that the mechanic pressure on the area of the missing tooth ceases, resulting in the thinning of the bone. If we intend to have an implant to fill our absent tooth or teeth, under the condition of bone defects there is insufficient bone for the new tooth. In such cases, bone grafting is the solution, as the missing tooth can be replaced without any difficulties after the process. Bone augmentation may also be necessary after the removal of a cyst or a dental root and in order to stabilize the loosened teeth of patients suffering from periodontal disease.
What risks are involved?
Thanks to the advanced technology used in the process, the risks involved are minimal. Of course, like in other medical interventions, certain complications may still occur. One such problem may be that the substance used for replacing the bone does not properly grow together with the own bone. Should this happen, the artificial material is removed and another surgery is carried out to deal with the issue. The problem is not a frequent one, so the intervention can be considered safe and efficient.
What types of bone grafting are there?
We can distinguish between the following bone graft types:
- Sinus lift
- Vertical bone graft (jaw bone lift)
- Horizontal bone grafting (jaw bone augmentation)
- The combination of the above
- Filling of bone defects
The type of intervention and the bone replacement material depends on the condition of the patient and the purpose of the operation.
In most cases, a bone graft is necessary in case of the replacement of the upper molars with implants. The upper molars are so close to the sinuses that their roots may reach it, so the implants would protrude the bone. If this is the case, the dental surgeon performs a so-called sinus lift before filling the bone with bone substitute. When an open sinus lift is performed, the specialist inserts the bone graft material through the patient’s jaw bone, while in case of a closed sinus lift, the intervention is carried out from the area of the missing tooth.
Vertical/horizontal bone grafting means the increasing/extending of the jaw bone by bone-spreading. During the intervention, the specialist inserts the bone graft material into the socket of the open jaw bone.
Filling bone defects is required after the removal of a large cyst from the oral cavity.
In each intervention, the area in question is covered by a special membrane after the insertion of the bone graft material. Ossification is a process that takes longer than the healing of the gums; thus, without the application of this membrane, the bone density would be occupied by the gums, making the intervention pointless.
Costs of dental bone grafting
What influences the costs?
When it comes to bone grafting, the general calculation of expenses is a challenging task, as each case is unique most of the time. The total cost is basically calculated based on the amount of bone grafting, the type of intervention, and the material costs.
The actual price of the intervention is made up of:
- the cost of the surgery
- the cost of bone grafting material used
- the cost of the membrane used
during the surgery. The costs of surgery depend only on the type of intervention. The amount of materials used is always determined per unit.
In case of synthetic bone graft materials, costs are calculated per gram, while in the case of the membrane, the calculation of costs is based on the amount or area.
Different types and costs of dental bone grafting:
- Sinus lift: During this procedure, the dental surgeon lifts the sinuses and inserts the dental bone graft material between the jaw bone and the sinuses. The surgical cost of a sinus lift is calculated per jaw side and the dental bone grafting costs are based on the number of necessary units to fill up the bone. The operating costs of a sinus lift are 495$/jaw sides. The bone replacement material (bone of animal origin or synthetic bone) costs 98 $/unit.
- Vertical/horizontal bone grafting: Increasing/extending of the jaw bone by jaw bone-spreading. Here, we calculate the costs per necessary unit to ensure enough bone for an implant. One unit costs 98$. For example, if two units are necessary for a position for implantation, the costs are 196$ in total.
Are bone grafts covered by insurance?
The costs of bone reconstruction are not covered by statutory health insurance, except in very rare cases. Private health insurance (PHI) may even cover the cost of the entire treatment.