However, periodontitis does not appear naturally, it frustrates many people’s lives, especially the middle-aged and the older generations. Our article shows its causes, nature; also gives useful tips on how to prevent or cure it.
From our article you can learn the following:
- What is periodontal disease?
- The symptoms of periodontitis
- Who are more at risk of periodontal disease?
- What factors lead to periodontitis?
- How to avoid periodontitis?
- The treatment of periodontitis
What is periodontal disease?
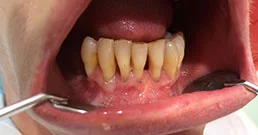
Periodontal disease (also known as periodontitis or gum disease) is one of the most common defects of the gum and its tissues. Many adults suffer from this inflammatory condition of the gum and bone support. Its initial stage is the inflammation of the gum at the necks of the teeth. The medical term for this inflammation is gingivitis). Gingivitis, when not dealt with in time, can lead to periodontitis. The result is a reduction in the gum tissues. Since the teeth lose their supporting tissues with time they loosen and eventually fall out or must be pulled ohe symptoms of periodontitis?
The symptoms of periodontitis
Most of the symptoms are easily recognizable although there are some other alterations. Let’s check them in details!
Red swollen gums, unpleasant breath.
The gum becomes red and swollen because of the inflammation, and it bleeds on touching (e.g. when brushed). Decaying tissues cause bad breath. The inflamed gum recedes, thus exposing more of the tooth neck.
Loose or lost teeth.
On the long run the teeth loosen, then they fall out.
Other invisible problems.
We can perceive inflammation, bad breath and the exposure of the teeth thorough the senses. However, only a dental examination can establish the extent of the damage to the tooth enamel, the gum tissues and the bone.
What is about pain?
Have you noticed that pain is not among the symptoms? Since this inflammation does not usually cause any pain, most people only visit their dentist when their gum is visibly damaged. This is a mistake. You should practice correct oral hygiene and have regular dental exams. This way the dentist can frequently remove plaque from your teeth. These are the best ways of preventing periodontal disease.
Who are more at risk of periodontal disease?
The periodontal disease mostly occurs in the middle-aged or the elderly, while gingivitis is most frequent at younger age. Gingivitis in itself does not cause lasting damage. Also, a timely and proper treatment can prevent further damage to the gum. Learning and maintaining proper oral hygiene plays a key role in the preventing process.
What factors lead to periodontitis?
The main causes of periodontitis can be categorized as follows:
Increasing of the number of bacteria
The basic reason are the bacteria present in the person. Depending on the physiology of the individual and on their oral hygiene, a film of bacterial plaque forms on the teeth. When the person neglects careful brushing and rinsing, this plaque becomes thicker and the bacteria it hosts starts attacking the enamel and inflaming the gum.
Improper oral hygiene
Besides poor hygiene, a number of other factors can play a role: brushing one’s teeth too hard or using the wrong movements with the toothbrush.
Lifestyle, diseases
Smoking and diabetes also increase the risk of inflammation. In some cases genetic factors and hormonal changes play a role as well.
How to avoid periodontitis?
Mostly with early detection and proper oral hygiene.
Gingivitis, the former step before periodontitis, can be completely cured. However, if periodontitis commences, serious medical treatments are necessary. If it advances, osteoporosis may appear; as a consequence, treatments lengthen and patients would need a bone graft.
In case you have an illness (diabetes, osteoporosis etc.) that makes you susceptible to periodontitis, go for regular check-ups.

The treatment of periodontitis
The first step is learning proper oral hygiene (brushing and flossing), since by neglecting this the patient undermines any kind of past and future dental treatment.
The next step is removing the bacterial plaque. Depending on the type and amount of the plaque, the patient may need repeated treatments. This of course means a longer healing process. Irregular fillings or poorly executed bridges or crows can host bacteria as well, so these must be repaired. In certain cases the patient may need braces. This occours when the teeth are too close to each other, therefore they are difficult to clean properly.
If the symptoms persist, a dental x-ray can reveal the damage in the gum and teeth. Based on the findings, the dentist can use special techniques for cleaning and disinfecting the so called pockets (the space between the teeth and the gum where bacteria can hide). These procedures take place under local anesthesia. In more advanced stages of the disease, the roots need cleaning as well. During a surgical intervention your dental professional separates the gum from the teeth for a deeper cleaning procedure. Besides these techniques, plastic surgery interventions are used as well, but they take more time and can be more expensive, depending on the materials used. All types of treatment aim at strengthening the gum and preserving the teeth.
In summary, periodontal disease or periodontitis is one of the most commonly present diseases among the adult population. But just because it is common, you cannot take it lightly. Regular dental examinations and proper oral hygiene have a key role in preventing or containing this disease. Dental surgery can treat the consequences of advanced periodontal disease, so the best idea is to contact your dentist no matter at which stage of periodontitis you find yourself.